2023-04-11
Hyperbilirubinemia is mainly caused by bilirubin metabolism or circulatory disorders, and can be clinically manifested as hyperunconjugated bilirubinemia and hyperconjugated bilirubinemia. Gilbert syndrome and Dubin-Johnson syndrome are common genetic factors leading to hyperbilirubinemia. The former is caused by the UGT1A1 gene mutation, which mainly increases unconjugated bilirubin; the latter is caused by the ABCC2 gene mutation, which mainly binds Mainly elevated bilirubin.
Recently, a study entitled "Concurrence of novel mutations causing Gilbert's and Dubin–Johnson syndrome with poor clinical outcomes in a Han Chinese family" published in the Journal of Human Genetics reported a rare case of Gilbert syndrome combined with Dubin -Families with hyperbilirubinemia due to Johnson syndrome.

Basic family information
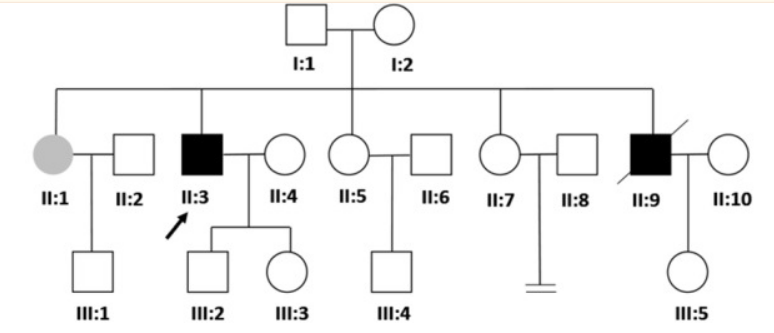
The proband (II:3) developed unexplained skin and sclera yellowing after birth, and developed pleural effusion, ascites, pericardial thickening, intrahepatic and extrahepatic bile duct dilatation, and gallbladder enlargement at the age of 50, but liver ultrasound examination showed no abnormalities . Epstein-Barr virus, cytomegalovirus and hepatitis virus serological tests were normal. Total bilirubin 164 μmol/L (3.0-21.0 μmol/L), direct bilirubin 133 μmol/L (0-7.0 μmol/L), indirect bilirubin 31 μmol/L (1.7-14.0 μmol/L) .
The younger brother of the proband (II:9) also developed unexplained yellowing of the skin and sclera after birth. He developed chronic cholecystitis and cholelithiasis at the age of 43 and took Xiaoyan Lidan Tablets regularly. In addition, long-term use of amlodipine and metoprolol to control blood pressure. He developed cirrhosis and primary liver cancer at the age of 48 and died shortly thereafter. The patient was diagnosed with hepatitis B at the age of 18, but it resolved spontaneously. At the age of 46, total bilirubin was 63.5 μmol/L (3.0-21.0 μmol/L), direct bilirubin was 45.8 μmol/L (0-7.0 μmol/L), indirect bilirubin was 17.7 μmol/L (1.7-14.0 μmol/L).
The sister of the proband (II:1) had total bilirubin 30.8 μmol/L (3.0-21.0 μmol/L), direct bilirubin 24.5 μmol/L (0-7.0 μmol/L), indirect bilirubin 6.3 μmol/L L (1.7-14.0 μmol/L), without clinical symptoms. The liver function indexes of other family members were within the normal range.
Genetic testing pinpoints rare causes
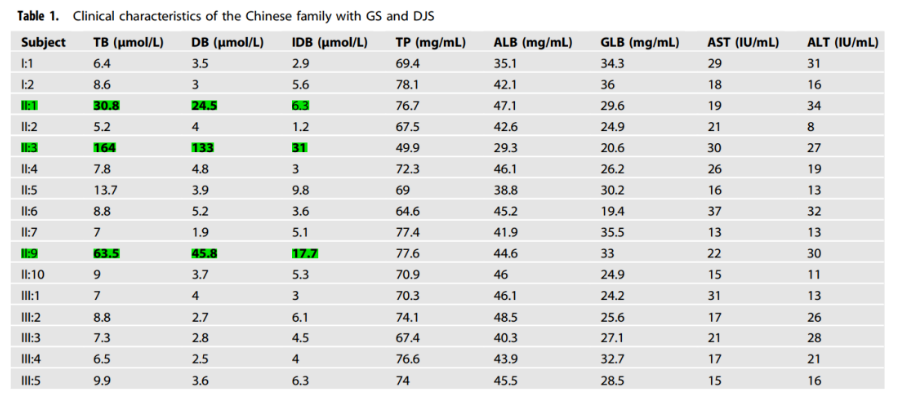
The researchers conducted sequencing analysis of the Gilbert syndrome UGT1A1 gene and the Dubin-Johnson syndrome ABCC2 gene in this family member, and the results showed that:
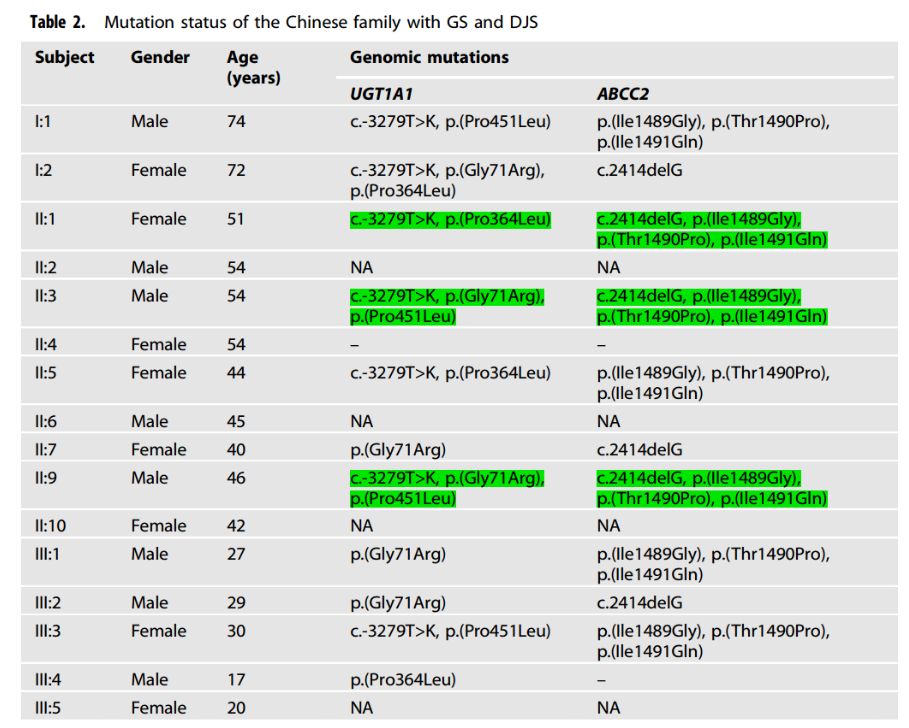
The c.-3279T>G (paternal), c.211G>A (maternal) and c.1352C>T (paternal) mutations were detected in the UGT1A1 gene of the proband (II:3), all of which were heterozygous; ABCC2 The c.2414delG (maternal) and c.4465_4473delinsGGCCCACAG (paternal) mutations were detected in the gene, both of which were heterozygous.
The younger brother of the proband (II:9) was consistent with the results of genetic testing of the proband. The c.-3279T>G (maternal) and c.1352C>T (maternal) mutations were detected in the UGT1A1 gene of the proband's sister (II:1); the c.2414delG and c.4465_4473delinsGGCCCACAG mutations were detected in the ABCC2 gene.
Based on previous studies on the effect of UGT1A1 gene variation on enzyme activity[2], pathogenicity analysis of ABCC2 gene, and family co-segregation, the proband (II:3) and his younger brother (II:9) had Gilbert syndrome combined with Dubin - In a patient with Johnson syndrome, the sister of the proband (II:1) is a patient with Dubin-Johnson syndrome, and the mother of the proband (I:2) may also be a patient with Gilbert syndrome. All other family members were carriers of UGT1A1 or ABCC2 monoallelic variants.
Summary
Based on previous studies on the effect of UGT1A1 gene variation on enzyme activity[2], pathogenicity analysis of ABCC2 gene, and family co-segregation, the proband (II:3) and his younger brother (II:9) had Gilbert syndrome combined with Dubin - In a patient with Johnson syndrome, the sister of the proband (II:1) is a patient with Dubin-Johnson syndrome, and the mother of the proband (I:2) may also be a patient with Gilbert syndrome. All other family members were carriers of UGT1A1 or ABCC2 monoallelic variants.