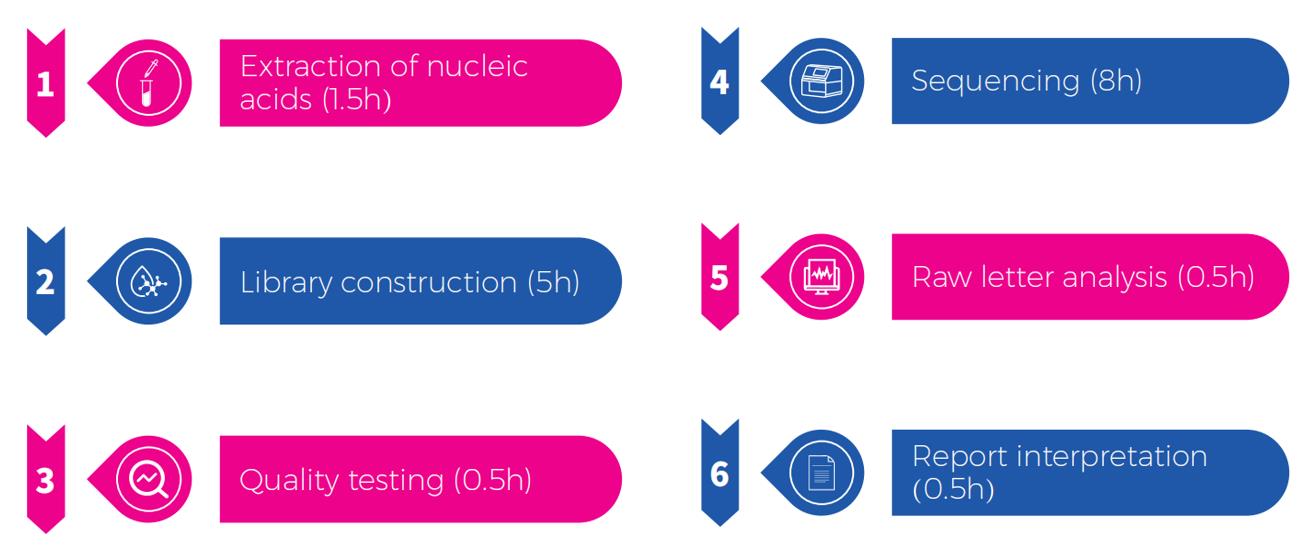
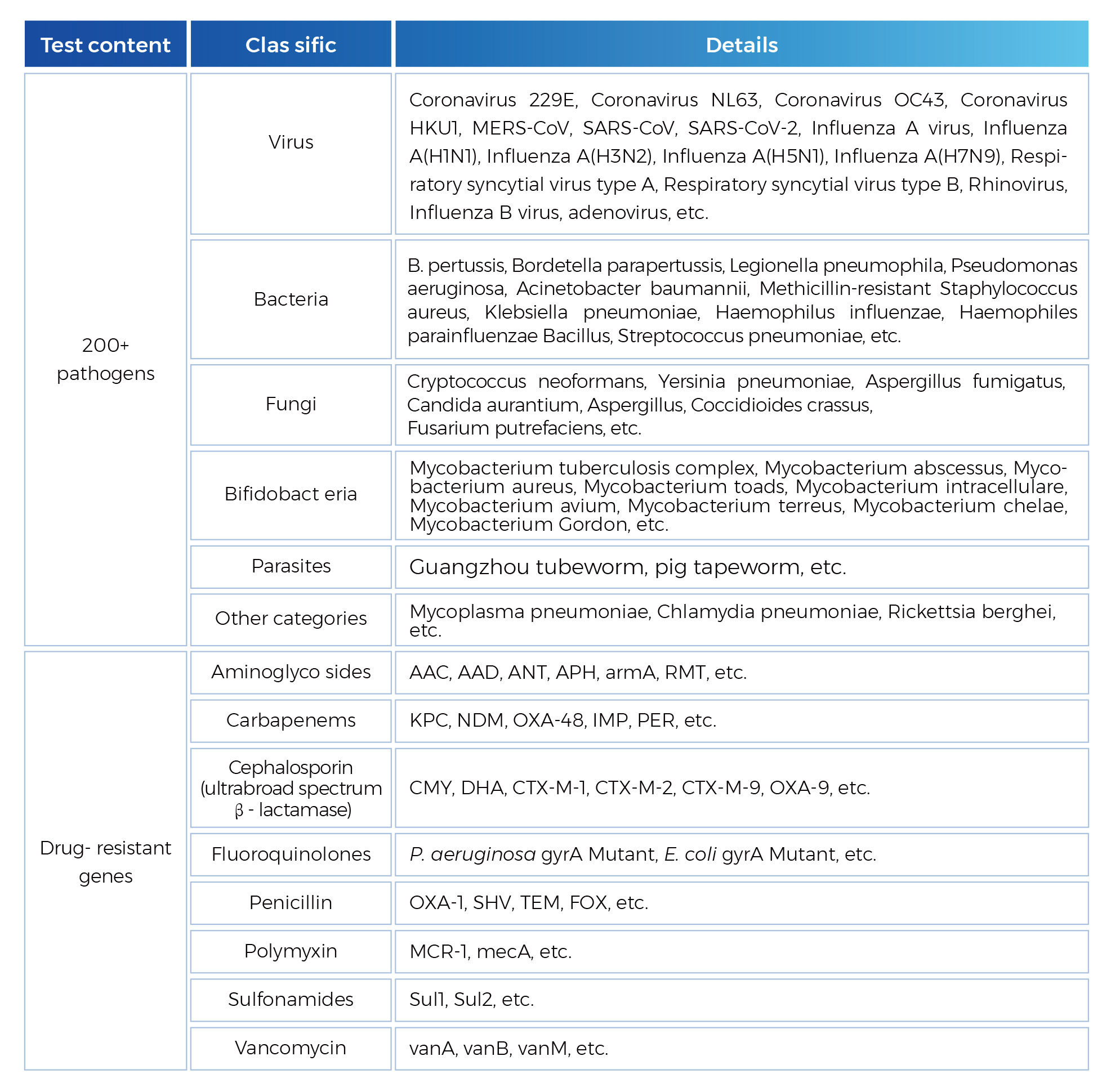
Uni-meidca pathogens targeted Next Generation Sequencing(tNGS), using the patented "All-In-One" ultra-high-weight PCR amplicon capture technology and next generation sequencing technology, high-precision detection of trace pathogens nucleic acids in samples, not only can quickly identify viruses,bacteria, fungi, parasites and other pathogenic Microorganisms, but also can detect multiple drug resistance genes, which can help the rapid identification and detection of pathogens.


TAT<16h

● Clinical information:The patient, male, 49 years old, was admited to the hospital with "fever with chest tightness and shortness of breath for 3 days". The chest CT indicated multiple nodules and lumpy shadows in his both lungs, and recurrent fever and shortness of breath in the chest worsened despite conventional broad-spectrum anti-bacterial and viral infection treatment.The patient took long-term oral glucocorticoid therapy for immune thrombocytopenia.
● Routine Pathogensy: Sputum culture and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid culture did not reveal signs of bacterial or fungal infection, and sputum antacid staining did not reveal tuberculosis.
● tNGS testing: On the 10th day of admission, alveolar lavage fluid was taken for pathogens targeted NGS testing. 48 hours later, the results reported mixed infection with Yersinia pneumoniae and cytomegalovirus, with sequence numbers of 923 and 137. After anti-infection regimen was adjusted, the temperature decreased to normal.
● Point of view: Pneumocystis jirovecii and cytomegalovirus in respiratory specimens cannot be identified by routine culture, and the process of samples testing by staining microscopy, PCR amplification, and molecular immunological
takes a long time. The process is complicated, and the number of detectable pathogens is small, which will cause serious delays in both etiological diagnosis of infectious diseases and treatments. Pathogens targeted NGS detection can
make up for the insufficiency of the above conventional methods, and can identify
pathogens earlier and quicker, which is benefit for providing an etiological basis for timely and accurate treatment of severely infected patients.